Web3 and Decentralized Finance: Fintech 4.0
The Decentralization Revolution
The decentralization revolution began with the invention of Blockchain in 2008 by Bitcoin’s creator Satoshi Nakamoto. Blockchain is the underlying technology of Bitcoin and combines cryptography, economics, and finance. Satoshi created a system for currencies which is:
Trustless - no need to trust any participant in the network; instead they are incentivized by the economic mechanism design of Bitcoin mining to behave appropriately
Immutable - the use of cryptography makes it hard to remove or change the data; this also means that transactions on the blockchain are generally tamperproof
Hard to Fraud - fraudulent activities can be easily checked against the immutable blockchain data
The most interesting part of blockchain though is its decentralized nature. This allows systems such as those for payments to run without central authority. It allows transactions to happen directly in a peer-to-peer nature without having to go through an intermediary. It also allows all participants of the network to partake in its operations and governance; making it democratic. This very nature of blockchain makes it revolutionary and gives it the potential to re-engineer the way many systems run today. Financial services are of particular interest as distrust in financial institutions and governments increases globally.
One of the key use of blockchain is its use to tokenize assets, this can be linked to a real-world asset or digital ones. The owner of the digital token can directly hold these tokens in their digital wallets and need not have to deposit it in custody with a bank or stock exchange. Some examples of assets that can be tokenized are:
Currencies
Stocks, Bonds and other financial
instrumentsReal Estate
Fine Art
Another important aspect of blockchain is its ability to run smart contracts or code autonomously and in a transparent manner. This gives even more ability to replace traditional intermediaries as smart contracts can automate actions and processes; replacing existing centralized functions. Smart contracts already exist to replace:
Exchanges and Marketplaces
Custodianship or Escrow
Organizations and AGMs
Decentralized Finance
With its various features, blockchain is a prime technology to disrupt financial services. Decentralized finance refers to financial ecosystems that bypass traditional financial intermediaries by combining digital assets and smart contracts on blockchain technology. This creates greater transparency for financial transactions; and democratizes access and ownership to financial assets. It also gives access across borders; in particular to the global unbanked.
Since the inception of Bitcoin, DeFi has grown in its use cases and applications
How does DeFi compare to traditional finance? We can make a comparison here.
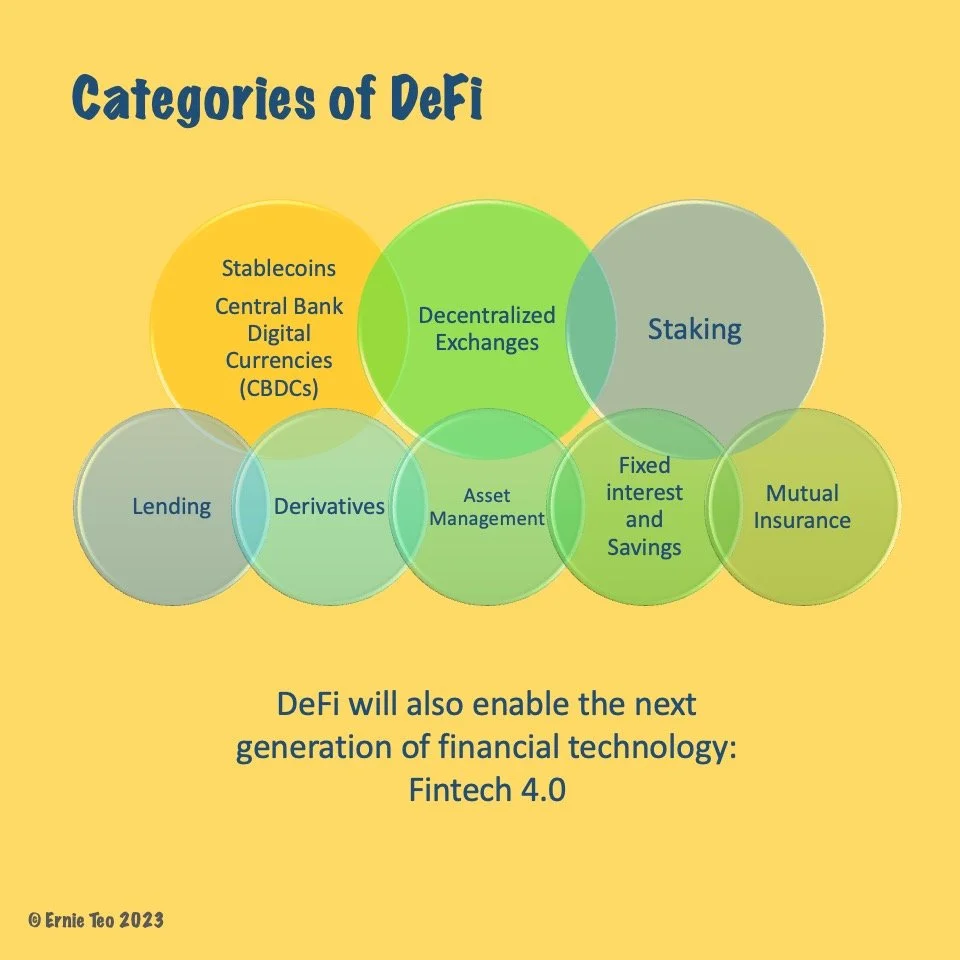
There are many categories of DeFi. Beyond the basics of cryptocurrencies, decentralized exchanges, and staking, it has been applied to many traditional areas of finance.
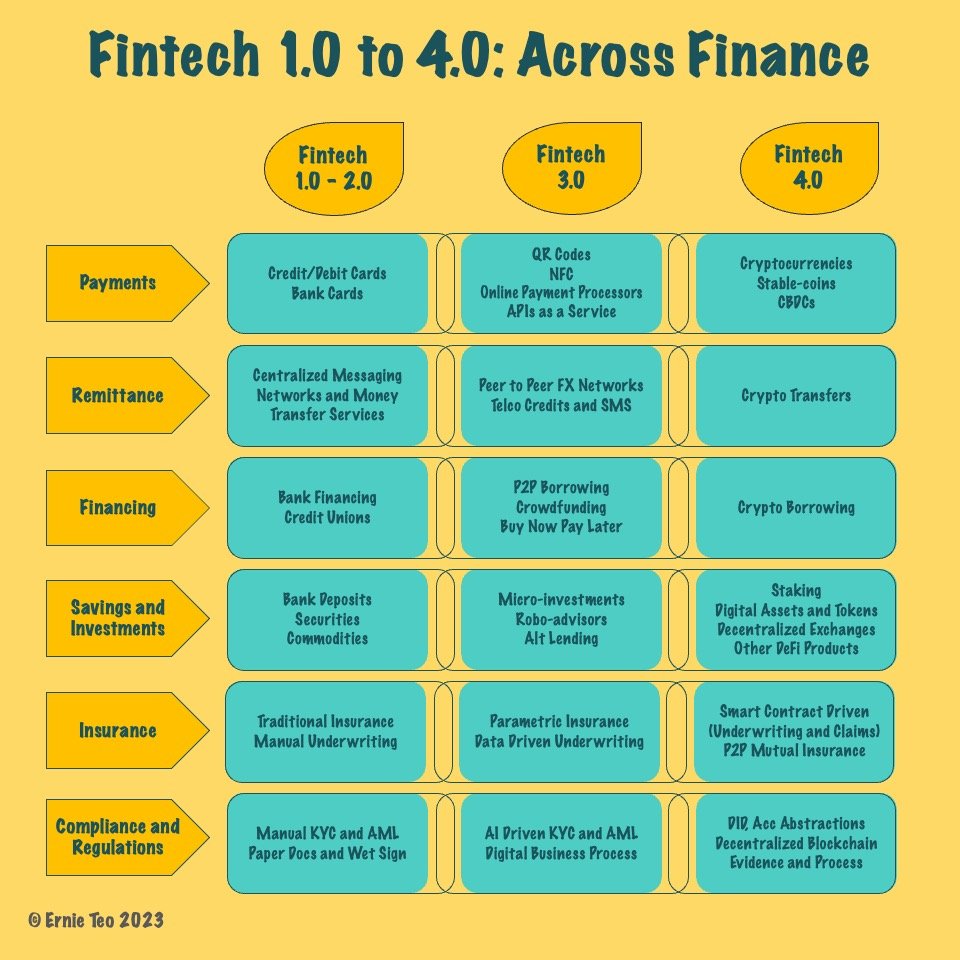
Evolution of Fintech: One to Four
Technology has been used by the finance industry since the 1960s and “fintech” has gone through many iterations. DeFi is part of Fintech 4.0 where the focus is on empowering users.
Here are some examples of how Fintech has moved through its various iterations:
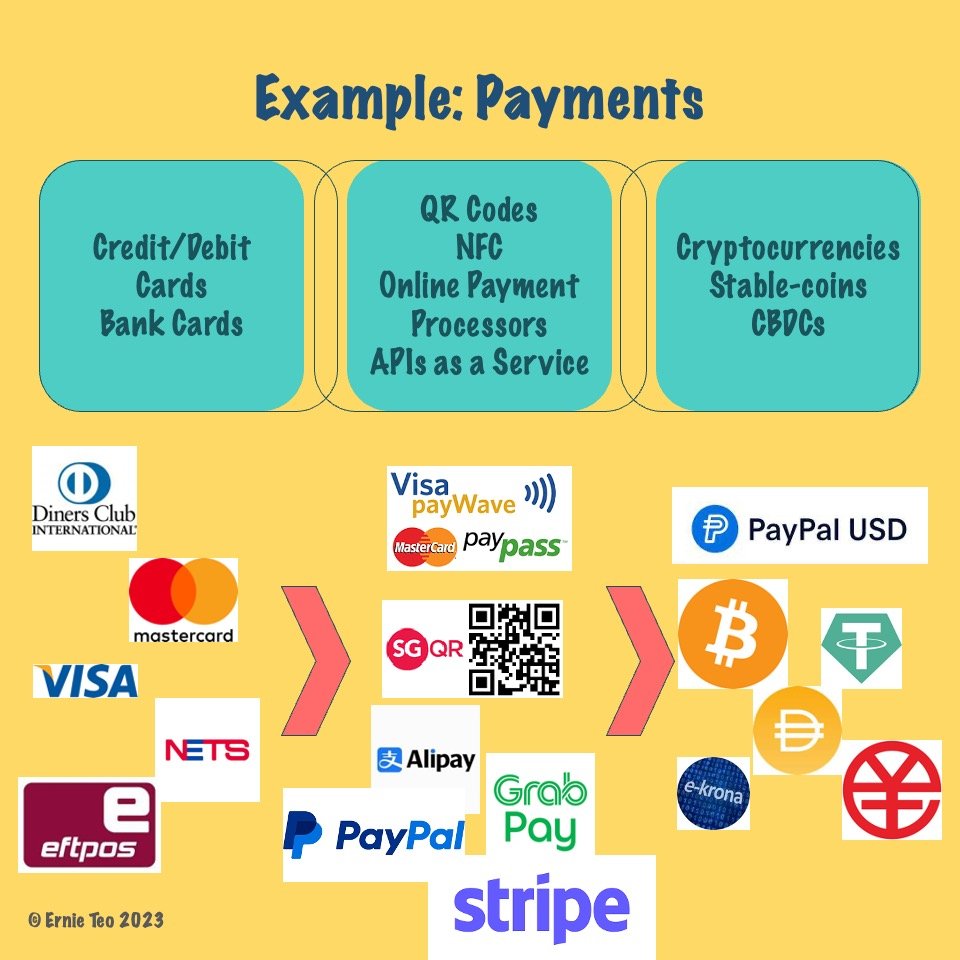
We have moved from more traditional card processing systems and electronic transfer systems for payments; to the use of QR codes, NFC, and APIs. Will the future be in digital currencies?
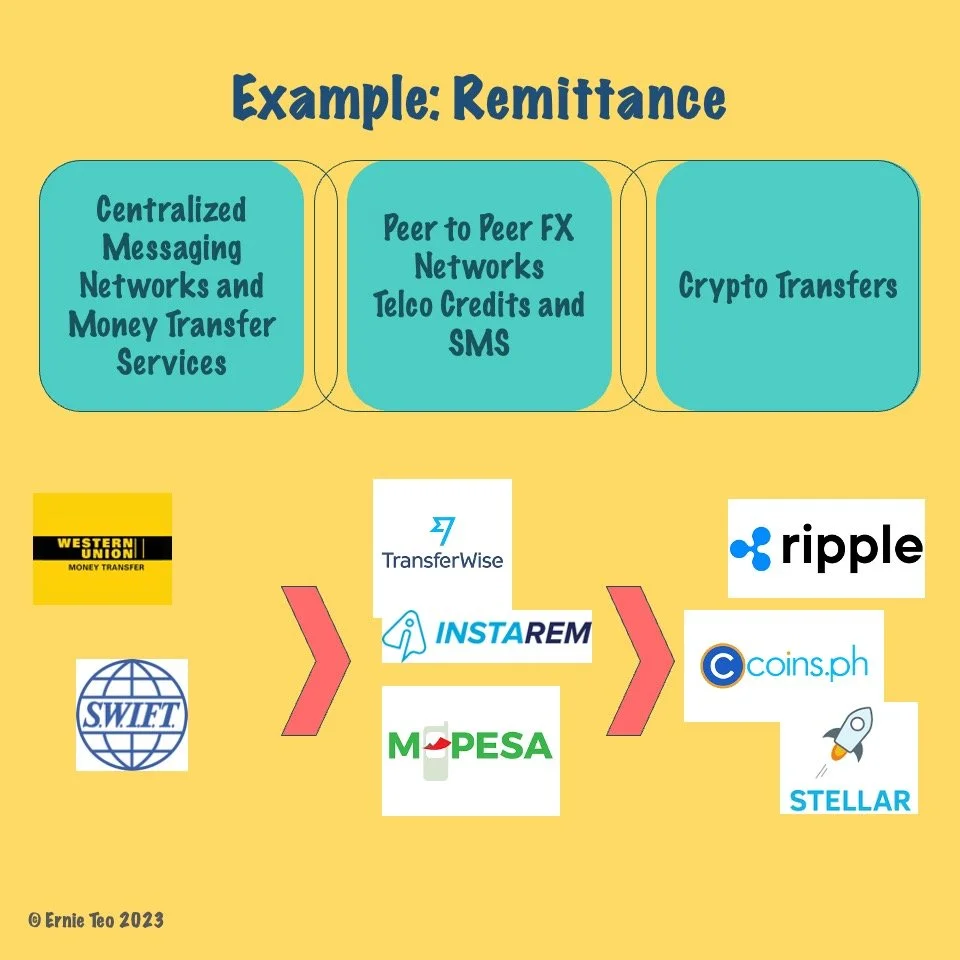
Inefficient remittance networks are being disrupted with peer-to-peer FX networks like Wise. Crypto and blockchain transfers could be the way forward.
Conclusion: The Future
Although Web3 and AI will change the way that financial services will be offered, it is still early days in terms of it being operational. There are many kinks that will need to be ironed out especially those revolving around regulations and policy. There could be many possibilities for the future of fintech. There could be full decentralization and democratization. In this future, full responsibility is on asset owners and the ecosystem needs to self-regulate in an autonomous manner which can be hard to achieve. A more realistic future is probably one where we find a middle ground between DeFi technologies and regulatory oversight. The challenge is definitely ensuring that the economy and consumers are protected while not stifling financial innovation.